Types of resistors (Fixed and Variable, 2025)
Resistors come in various types, each with unique characteristics and applications. Two primary categories of resistors are fixed and variable.
Resistors come in two main types: fixed, with a predetermined resistance value, and variable, whose resistance can be manually or electronically adjusted. Both types have further subcategories for specific types.
In this article, we’ll explain the types of resistors in detail.
Types of resistors
When you are working with electronic circuits, you need to know about various components such as resistors basics, inductors, capacitors, battery sources, connecting wires, transistors, and many more.
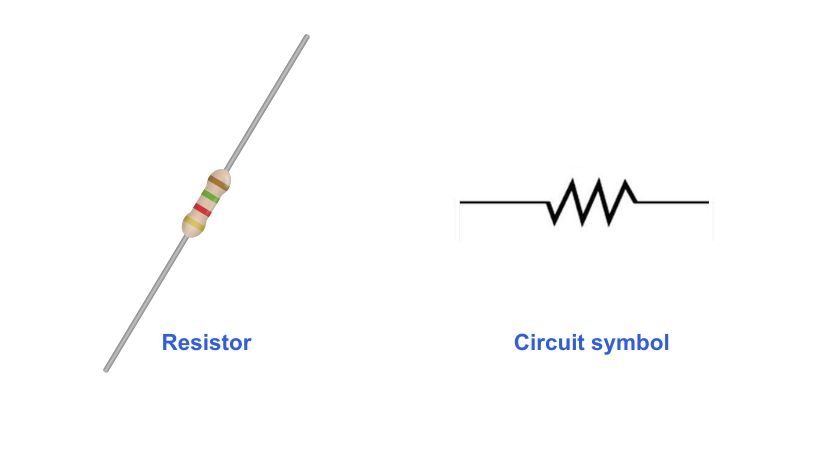
The resistor is the fundamental component of the circuit. A resistor is defined as,
A passive electrical component has two terminals that are used in electrical circuits to control or limit the flow of electric current.
When there is no resistor, a high amount of current will flow through the circuit which may damage the load such as a bulb or fan, etc., and the whole circuit becomes unfunctional.

But if the recommended value of the resistor is connected to the circuit it will limit the flow of current in the circuit and will provide the desired flow of current to the load.
There are several types of resistors and each one has its construction and characteristics.
There are two main types of resistors: variable resistors and fixed resistors. Both types of resistors have specific uses in electronic systems.
Remember before learning about different components make sure to learn about the basics of electronics.
1. Fixed resistors
A fixed resistor is a type of resistor that has a fixed or predetermined value of resistance. We can not change the value of the fixed resistor.
There are various types of fixed resistors. Let’s discuss all these types.
a. Types
Here are some types of fixed resistors.
1. Carbon composition resistors
A blend of granulated or powdered carbon or graphite, insulating filler, and resin binder is used to create a carbon composition fixed resistor. This is the most common type of fixed resistor.

The actual resistance of the resistor depends upon the amount of insulation material in the composition. They have cylindrical shapes and are cost-effective.
They are appropriate for low-frequency applications, although their accuracy, stability, and noise performance are limited.
2. Wire wound resistors
A resistive wire, frequently a nickel-chromium alloy, is coiled around a ceramic or fiberglass core to create wire-wound resistors. Some other alloys such as tungsten, manganin, nichrome, or nickel are also used.
These resistors are costly as specific alloys used in them are expensive. They come with power ratings ranging from 2 watts to 100 watts or more. These resistors range in ohmic value from 1 ohm to 200k ohms or more.
They are commonly used in power electronics, high-frequency circuits, and applications where high precision is required.
3. Thin film resistors
A resistive substance and a high-grid ceramic rod are the main components of all thin film resistors.

In these resistors, a very thin resistive film is deposited onto a ceramic or silicon substrate using physical or chemical vapor deposition techniques.
It has two types, a carbon film resistor and a metal film resistor. High-grade ceramic material is the substrate, an insulating rod or core found in carbon film resistors.
Due to negligible noise and wide operating range, these resistors are mostly used in electronic circuits.
The metal film resistor has the same structure just like a carbon film resistor but the main difference is it has metal instead of carbon. They are very thin, cheap, and provide reliable operation.
4. Thick film resistors
As the name suggests these types of resistors will have thick film.
Thick film resistors are made using the same process as thin film resistors; the only distinction is that a thick film is used in place of a thin film or layer of resistive material.
They are cost-effective and widely used in consumer electronics. However, they have relatively low power ratings and are suitable for low to high-power applications.
b. Advantages
Fixed resistors offer some very essential advantages. Some of the advantages of fixed resistors are as follows.
- Fixed resistors offer consistent and stable resistance values, maintaining their specified resistance over time and environmental conditions.
- Due to their static resistance value, they offer a high level of reliability and reduce the likelihood of failure within the circuit.
- They are often more affordable compared to a variable resistor, which makes them a cost-effective choice for various applications.
- They are appropriate for situations when there is a shortage of space because they come in small sizes.
- The implementation of these resistors is simple as they have fixed resistance values.
c. Disadvantages
There are also some drawbacks of fixed resistors.
- We can not change the values of resistors as they are fixed so there is no means of adjusting resistance which limits its applications.
- Due to their fixed resistance, they cannot adapt to changing circuit requirements or tuning needs.
- Fixed resistors can lose excess power and become inefficient in applications where a precise resistance value is not required.
- They have tolerance limitations, which means the resistor value might deviate from its stated value.
2. Variable resistors
As the name suggests, variable resistors allow one to adjust their resistance value. The value can be changed by using screw, knob, or dial.
These types of resistors have sliding arms and the value of the resistor can be changed by rotating it.
They are used in circuits where resistance needs to be varied manually or electronically.
a. Types
Let’s explore three common types of variable resistors:
1. Potentiometers
Potentiometers are three-terminal electronic devices that have a wiper—a movable contact—and a resistive element. The resistance value between one terminal and the wiper can be changed by rotating the wiper.
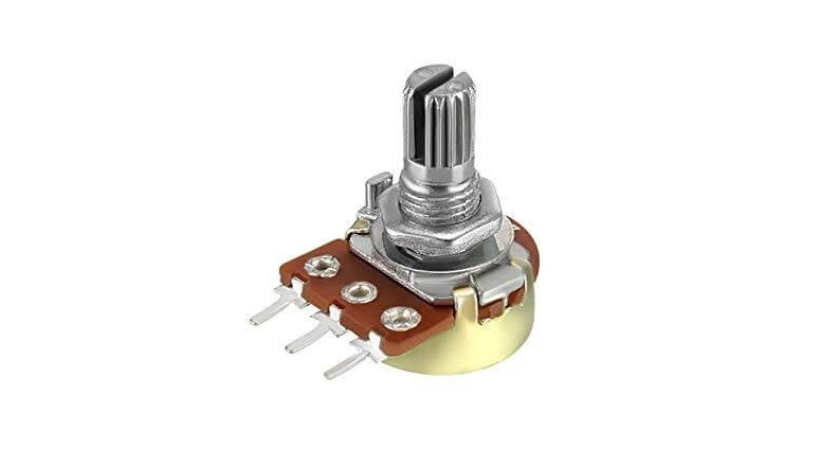

Potentiometers are used in circuit tuning, brightness control, and volume control applications. It can be used as a potential divider and they are available up to 10 Mega ohm.
2. Rheostats
The rheostats are also known as tapped resistors or variable wire wound resistors. It is a two or three-terminal device.
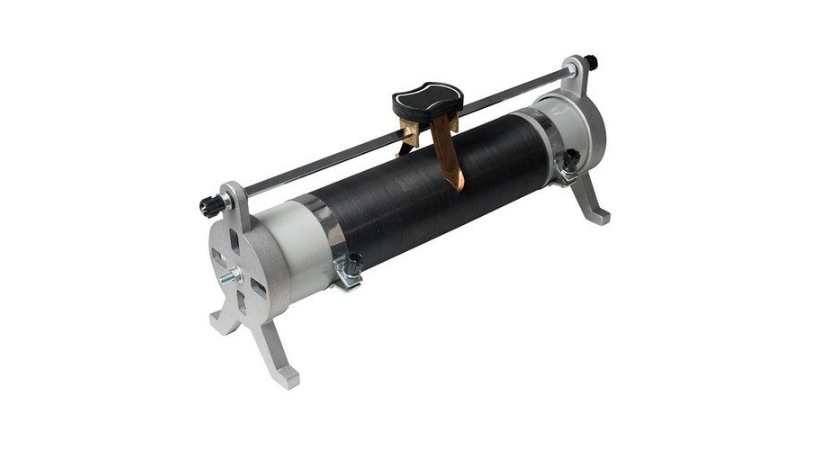

Rheostats are mostly used to modify the resistance of a circuit to control the current. They are frequently used in light dimmers, heating components, and motor speed control.
3. Trimmers
Trimmers are usually small, compact components that consist of a resistive element and a movable contact. It is also called a trimmer resistor or trim pot.
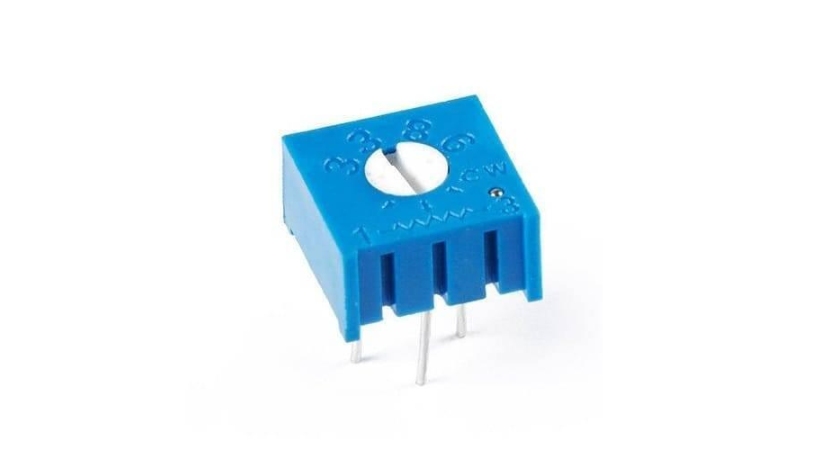

With a tiny screwdriver, you may adjust the screw’s location so that it rotates, changing the resistance value. They are available in different resistance and power ranges.
They provide a convenient way to adjust the resistor value to gain precision and fine-tuning.
b. Advantages
Let’s discuss the advantages that are offered by variable resistors.
- With variable resistors, you may change the resistance in a circuit to change the amount of current or voltage.
- Variable resistors offer versatility in different applications by providing adjustment in the resistance value.
- Similar to potentiometers, some variable resistors have changeable outputs, which makes them useful for voltage dividers, volume controls, and other applications that need flexible outputs.
- By offering a wide range of resistance values, the variable resistors can adapt to changing circuit requirements.
c. Disadvantages
With lots of benefits, there are also some disadvantages of variable resistors.
- Due to mechanical wear and aging, variable resistors might have lower stability as compared to fixed resistors.
- The adjustable feature of the variable resistor makes it a little bit expensive.
- The continuous changes or wear can lead to reduced lifespan or degradation in performance with time.
- Variable resistors might require more space within a circuit due to their larger size, especially certain types like rotary potentiometer
There are types of resistors, the choice of resistor for your circuit depends on the circuit requirements. Understand the circuit requirements before the selection of electronic components.
Conclusion
A resistor is an essential component in the electronic circuit that regulates or controls the flow of current by developing voltage in the circuit.
There are two types of resistors: fixed resistors and variable resistors. As the name suggests the fixed resistor has a fixed value of resistance and we can not change that value.
The fixed resistors are easy to use and cost-efficient and they also offer stability and reliability in the circuit. We can’t change the values of these resistors which make them inflexible.
On the other hand, variable resistors allow us to adjust the resistance value according to our own choice. They offer adjustability, versatility, and precision but due to mechanical wear or aging, they might have less precision and stability.
The selection of the type of resistor depends upon your project requirements.
This was all about types of resistors, I hope it will be helpful.
Thank you and stay blessed…
**These were resistor types; continue learning about resistors by exploring how to read resistor values like what color code is, etc.
