- Siglent sds1202xe – best versatile oscilloscope
- Rigol ds1054z – best budget oscilloscope
- Hantek dso5102p – best compact oscilloscope
These three beginner oscilloscopes consistently deliver quality, usability, and performance. These picks are popular in the electronics community for beginners and offer a balance of features that can easily take you from simple to intermediate projects.
| Parameters | Siglent SDS1202X-E | Rigol DS1054Z | Hantek DSO5102P |
| Bandwidth | 200 MHz | 50 MHz | 100 MHz |
| Channels | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| Sample rate | 1 GSa/s | 1 GSa/s | 1 GSa/s |
| Price range | ~$399 | ~$350 | ~$250 |
| Pros 👍 | Built-in waveform generator | Upgradable bandwidth | Easy operation |
| Cons ❌ | Too technical | Limited features | Basic functionality |
- The Rigol DS1054Z offers excellent value for its price. It has a user-friendly interface, making it easy for beginners to learn how to use an oscilloscope effectively. Plus, the upgradeable bandwidth gives users room to grow as their needs become more advanced.
- The Siglent SDS1202X-E strikes a good balance between advanced features and usability. It’s versatile enough for various projects, including electronics and signal testing. The included waveform generator is a fantastic bonus for hands-on learning.
- The Hantek DSO5102P is compact and lightweight, making it ideal for beginners who need portability. It’s straightforward to use and perfect for students or hobbyists who want to test circuits on the go.
Let’s get into the details.
List of best oscilloscopes
Well, I cannot emphasize enough how much a quality oscilloscope is the basic need of every electronics hobbyist, beginner, or person involved in electronics.
Professionals recommend the Rigol DS1054Z or Siglent SDS1202X-E as the best oscilloscopes for beginners. They are the best value and price. Thousands of beginners have used them and are pretty satisfied with their quality and performance.
After reviewing and filtering many options, I finally settled on the three best oscilloscopes. I chose the Siglent SDS1104X-E.
1. Our Pick: Siglent SDS1202X-E
After intense research and my own experience, I concluded that the Siglent SDS1202X-E (Amazon link) is the best beginner oscilloscope. It is expensive, but it is accurate, solid, and has all the safety features that a quality oscilloscope must have.
The Good
Following are some excellent aspects of SDS1202X-E:
It comes from a known brand: Siglent Technology is new to the oscilloscope industry, but its models are reliable and affordable. I researched every model, read people’s reviews, saw videos, and used my own engineering knowledge to compare it with other brands.
The overall feeling of SDS1104X-E is good: You can’t describe this in words, but you know when you hold a quality product in your hand you just kinda feel it. And I had those feelings with this device.
Feature rich: This oscilloscope provides excellent value for its price. With a bandwidth of 200 MHz and a sampling rate of 1GSa/s, it captures signals accurately, making it suitable for a range of applications, especially for hobbyists and students.
User friendly design: Let me highlight the ergonomic design and the large 7-inch WVGA LCD screen, which is non-reflective and easy to read. The layout of controls is intuitive, which simplifies operation for beginners.
Advanced measurement capabilities: The oscilloscope includes features like Super Phosphor Oscilloscope (SPO) technology, Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) for spectrum analysis, and various automated measurements for parameters such as amplitude and duty cycle. This makes it a versatile tool for both learning and practical application.

Inner PCB and fusing: The PCB is appropriately masked, and holes are properly drilled. Also, there is a silkscreen for labeling, which further enhances the protection of copper traces. They are properly grounded, and the thickness of traces is good, which means they can withstand a large amount of power.

Low noise operation: Appreciate the low system noise, which helps in obtaining clear and accurate measurements without interference from background noise.
Serial decoding features: The SDS1202X-E supports serial decoders for protocols like I²C, SPI, and UART, allowing users to analyze digital signals effectively. This feature is especially beneficial for those working on embedded systems or digital communication projects.
The Bad
These are some bad things about this oscilloscope but not deal breakers:
- Some of the advanced features and settings may be overwhelming for beginners. It might take some time to understand and utilize the scope’s capabilities fully.
- While it offers good features, the SDS1202X-E is more expensive than basic models, which might deter beginners on a tight budget.
The Downright Ugly
The one downright ugly of this meter is that:
Limited Community Support: Compared to more established brands, the online community for Siglent products is smaller. This can make finding troubleshooting tips or user guides more challenging.
2. Also Great: Rigol DS1054Z
The Rigol DS1104Z (Amazon link) is an excellent alternative for beginners looking for a reliable and feature-rich oscilloscope. With its 4-channel capability, this model allows for simultaneous analysis of multiple signals, making it ideal for more complex experiments as users gain experience. It boasts a 100 MHz bandwidth and 1 GSa/s sampling rate, providing robust performance for various applications.
Users appreciate the intuitive interface, which includes context-sensitive buttons that simplify navigation, along with a 7-inch display that clearly presents waveforms, enhancing usability. Additionally, its advanced features, like waveform recording and serial bus analysis, make it a versatile tool for hobbyists and professionals alike.
3. Also Great: Hantek DSO5102P
The Hantek DSO5102P (Amazon link) stands out as a budget-friendly option. It offers a 100 MHz bandwidth and 1 GSa/s sampling rate, which provides adequate performance for basic electronic tasks. Its 7-inch color display ensures good visibility of waveforms, which is particularly helpful for beginners learning to interpret signal data.
Users praise its user-friendly interface, which facilitates easy operation and makes it accessible to those new to oscilloscopes. While it may lack some advanced features found in pricier models, its combination of affordability and essential functionality makes it an appealing choice for those entering the world of electronics.
Selection parameters
The following are the parameters that I think you should understand about oscilloscopes.
a. Bandwidth
Bandwidth limits the scope’s ability to measure a signal. It shows the frequency range that the oscilloscope can accurately measure. According to IEEE 1057, bandwidth is defined as “the point at which the amplitude of a sine wave input is reduced by 3 dB (approximately 30%) relative to its level at a lower reference frequency.”
In other words, bandwidth is specified at the frequency at which a sinusoidal input signal is attenuated to 70.7% of the signal’s true amplitude. In summary, the more the bandwidth, the more powerful the oscilloscope is, and the more expensive as well.
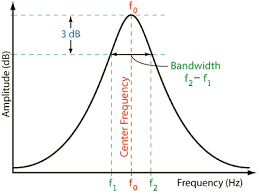
However, a rule of thumb for selecting a good bandwidth is to have the bandwidth five times greater than the fundamental frequency of your measuring signal.
That is a very good point for beginners. If you have high bandwidth and you are playing with a low-frequency signal, you do not get accurate results. Instead of excellent results, you get a lot of noise.
b. Sample Rate
The sample rate is the ability of an oscilloscope to how fast it can acquire the number of samples per second. Or in simple words, it determines the amount of waveform information captured and displayed on the screen. The greater the sample rate, the more resolution it has, and as a result, you have every detail of your signal on display.
SR = 2.5*(Highest frequency in the signal)
The above equation is the Niquest criteria for sample rate. Oscilloscopes must obey this to be called good or the best beginner oscilloscopes. This is an industrial-adopted rule of thumb.
However, some industry people also recommend a sample rate that is 3 to 5 times the bandwidth. The reason they provide is, that you need a high sample rate to see any unexpected glitches or anomalies. In summary, the more samples you have in each period, the more signal detail you’ll capture.
A good point to note is that without proper bandwidth, you will end up with an attenuated or distorted signal. Without enough sample rate, you will end up with no information necessary to display the exact frequency, rise, and fall times of your signal. You can also miss any glitch or anomaly occurring instantly.
One crucial thing to double-check is the sample rate of the oscilloscope when all channels are turned on. Typically, when multiple channels are in use, the sample rate is split up among the channels. If you are using more than one channel, you’ll want to make sure the sampling rate is still sufficient.
c. Memory Depth
Memory depth is the measure of the oscilloscope’s memory to store signals. More memory depth means you can capture signals at the highest sample rate. This is a very nice feature and a good oscilloscope must have a good size of depth memory. But it will make it costly.
The oscilloscope memory is directly tied to the sample rate. The more memory you have, the higher you can keep the oscilloscope’s sample rate as you capture a longer period of time. The higher the sample rate, the higher the effective bandwidth of the oscilloscope.
d. Waveform Update Rate
It is the time oscilloscope takes to update its screen. It is a significant feature to look for. Of course, who cares for an oscilloscope when it takes too much time to update its screen. As in such a situation, there is a good chance you may miss a vital signal or a sudden glitch.
The higher the waveform update rate (wfms/sec) is, the better the chances are of identifying any glitches in your signal, and therefore, you have a better oscilloscope.
e. Size and cost
The bench oscilloscope is used in the lab. Some people may use an oscilloscope for car diagnoses. For such people, who carry oscilloscopes everywhere, the size must be of great concern. The cost is a big issue.
But you cannot have a cheap oscilloscope with great features. It just cannot happen. Good bandwidth, sample rates, built-in wave generator, FFT, extra channels, and good memory depth are the parameters that will cost you money.
f. Number of channels
Two channels are more than enough if you are starting with electronics. The reason is that if you are going to use more than two channels, the extra channels will just make the scope expensive. For example, you want to see the communication of Arduino at the same time.
Two channels will be enough to see what is coming to your Arduino and what is going away from it, as well as to know the phase difference between two pulse trains or any two signals.
The key parameters above are what I think make the best oscilloscope buying guide. Besides these, there are features you should also take into consideration. Let’s talk about those in the following.
- Having a friendly graphical interface. There are a lot of scopes that have such ugly graphics that people find it very difficult to operate the scope accurately.
- Mathes functions, including FFT.
- External triggering
- USB storing option
- Remote controlling option
- Solid-body structure
- EMI/EMC free reading
- Low noise level
- High-quality probes to reduce signal distortion
Conclusion
An oscilloscope is a device that measures or analyzes changes in any electrical signal and studies the behavior of a system within its bandwidth limits. It displays an electrical signal with respect to time so you can see every detail of the signal, i.e., its shape, frequency, amplitude, and distortion.
Because the best reliable oscilloscope is so important that from day one, there are a lot of industry-leading oscilloscope manufacturers out there on the market, i.e., Tekpower, Keithley, Keysight, Aim-TTI, Rohde and Schwarz, and some new guys like Rigol, Hantek, Siglent Technologies, and GW Instek
Now, choosing the best beginner oscilloscopes or any level scope might be a little confusing for some guys, as there are many manufacturers, technical parameters to look for, and, of course, what you should pay for which feature.
And perhaps a lot of many more questions.
Here in this post, I try my best to help you find the best oscilloscope, whether you are a beginner, hobbyist, student, or professional.
I went through that deep research and found out that choosing the right oscilloscope can significantly enhance the learning experience for electronics beginners. While the Siglent SDS1202X-E stands out as the top recommendation, the Rigol DS1104Z Plus, and Hantek DSO5102P offer compelling alternatives that cater to different needs and budgets.
The selection of the best beginner oscilloscope depends on a few things and parameters.
It also depends on who you are, i.e., a design engineer to diagnose operational and design problems, an automotive engineer measuring the vibrations, a repair technician, or you’re simply trying to maintain your electronic pieces of equipment.
Answering the following questions first will be very helpful.
- What situation do you need a scope for? Where are you going to use it? For example, on the bench, at a customer’s site, or under the hood of your car.
- How many signals do you want to measure at once? For example, how many measuring channels will you require in your scope?
- A guess of the highest frequencies you will measure with the scope. In my opinion, you should be very sure of your frequency range when measuring the scope. This question is very important, so please pay close attention to it as it is directly in relation to the oscilloscope price tag.
- What are the amplitudes of your signals? If you don’t know, leave it. It is fine.
- Are the signals you are going to measure periodic or non-periodic?
Questions
Q1. How much bandwidth will you require?
Multiply your highest frequency by 5. For example, if your highest measuring frequency is 10MHz, then the ideal beginner oscilloscope would have a bandwidth of 50MHz.
For the said highest frequency, you can also use a scope with a 100MHz bandwidth, but it is not a good idea. It will cost you more money, and most importantly, you may end up getting a high noise floor as well. If you are not sure about the future, you can upgrade the bandwidth if needed.
Q2. How much sample rate will you need?
Follow the Nyquist criterion, which states that the sampling rate must be at least twice the maximum frequency that you want to measure. For example, if your maximum frequency is 10MHz, then the ideal scope for you must have a sample rate of 20MS/s. Again, a higher sample rate will cost more money.
Q3. Analysis & capture the random signals or glitches?
Will your projects involve the investigation of glitches? By glitches, I mean the small random impulsive signals that cause the sudden failure of a system. If yes, then select the one with a high waveform capture rate and high memory depth. The high wave upgrade can be a plus point here.
Q4. What resolution and accuracy do you need?
With an eight-bit resolution, you can detect a signal change of at best 0.4%. For applications such as audio, noise, vibration, and monitoring sensors (temperature, current, pressure), an eight-bit oscilloscope is often not suitable, so you should consider 12- or 16-bit alternatives. With a higher resolution oscilloscope, more accurate measurements are possible.
Q5. How are oscilloscopes priced?
Prices of oscilloscopes are based on many parameters but mainly on the following:
- The Bandwidth
- The Sample Rate
- Number of channels
- Memory depth
- Waveform update rate
The higher the above parameters, the higher the prices.
Q6. What are some famous oscilloscope brands?
Let’s talk about brands that make quality, best beginner oscilloscopes. Brand signals give feelings of trust. According to me, the higher the brand signals, the more quality product you get.
There are many manufacturers in the market. Not every one of them is good. There are also some bad manufacturers that we need to avoid if we want to invest a decent amount of money. The following are the brands that have proven themselves in the industry over the years.
- Tekpower
- Rigol
- Siglent Technologies
- Korad Technology
- Keithley
- Keysight
- Aim-TTI
- Rohde and Schwarz
- GW Instek
- BK Precision
They are global brands with a proven track record. I am sure if you are graduating from an engineering university, you may have seen a scope from these brands in your labs.
Keysight and Tektronix are indeed top-tier brands renowned for their precision, build quality, and advanced features. However, their scopes—especially entry-level models—often come at a premium price compared to other beginner-friendly brands like Rigol and Siglent.
Now, if I have confused you with too much technical stuff, forget about the rest and focus on the first two. The higher your bandwidth and sample rate requirements are, the higher you have to pay for a quality oscilloscope. And remember, there is no cheap oscilloscope.
Thank you, and have a good day!
Other useful posts:
**Disclaimer: Amazon links are affiliated, meaning if you decide to buy through the links, yamanelectronics.com may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you. This helps us a lot. Thank you.