The proper use and safety precautions consideration are necessary for the smooth and reliable operation of the diode.
To use a diode effectively, select one that meets project requirements, study its orientation, and identify its terminals. Ensure the forward voltage drop and reverse voltage are suitable, and avoid exceeding current or voltage limits to prevent damage. Follow safety measures like ESD protection, careful soldering, proper heat dissipation, checking polarity, and understanding component ratings.
In this article, we will discuss all the key points about how to use a diode properly.
Proper usage of the diodes
A diode is a component that allows current flow in one direction and blocks it in another.
To learn more about diode check out our article:
To ensure optimal performance and safety, it is crucial to understand how to properly use diodes.
Let’s discuss step-by-step how to use a diode properly.
1. Diode selection
The first step is the selection of the correct diode according to the application needs. Understand the application requirements such as applied voltage, power, and current.
Consider the diode’s specifications, including forward voltage drop (Vf), maximum forward current (If), and reverse breakdown voltage (Vr), to ensure compatibility with your circuit requirements.
2. Diode orientation
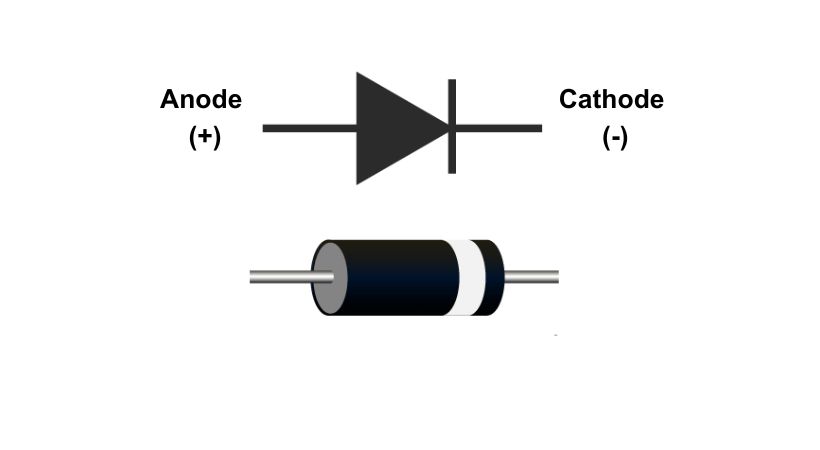
After the selection of the diode which is suitable for your application. Now it is time to identify the terminal of the diode.
The diode has two terminals named cathode and anode. The cathode is usually marked with a band or a notch.
It’s crucial to identify these terminals correctly because the diode’s behavior depends on the correct polarity.
3. Verify the polarity
You have identified the terminals of the diode it’s time to connect it. Make sure that the diode is inserted into the circuit with the proper polarity.
You have to connect the anode of the positive terminal of the battery and the cathode to the negative terminal of the battery.
Connecting a diode in reverse bias (with the polarity reversed) can result in blocking the desired current flow. Connect the diode is properly biased to allow the desired current flow in your circuit.
4. Forward voltage drop
To use the diode properly it is essential to consider the forward voltage drop rating of the diode. The forward voltage drop is the voltage required for the diode to conduct current in the forward direction.
For example, if the diode has a forward voltage drop of 0.7 volts and you want to power a device with a 5-volt power supply, you need to account for the 0.7-volt drop across the diode.
To avoid excessive voltage loss, it’s crucial to take this voltage drop into account while designing your circuit.
5. Maximum current rating
Understand and consider the maximum forward current rating of the diode for its reliable performance.
Diodes have a maximum forward current rating (If) that should not be exceeded. When working with a diode ensure that current passing through the diode does not surpass this limit to prevent damage or failure.
Consider using a diode with a higher current rating or adding current-limiting resistors if the current flowing through your circuit exceeds the diode’s rating.
6. Reverse voltage protection
The diode also has a reverse voltage rating means there is a recommended reverse voltage that a diode can handle without damaging itself.
Exceeding the reverse voltage limit can cause the diode to break down and conduct in reverse, potentially damaging the component or affecting circuit behavior.
Use extra protective devices, such as reverse polarity diodes or series resistors, or use diodes with the proper reverse voltage ratings.
Following these steps will help you to use a diode properly.
Diode safety measurements
You always need safety precautions while working with electronic circuits and components to protect yourself and your components from any damage.
Let’s talk about these precautions in detail.
1. ESD (Electrostatic discharge) protection
Electrostatic discharge can harm or even destroy diodes because of their sensitivity to it. Soldering the diode can cause electrostatic discharge.
Use an anti-static wristband or mat when handling diodes to avoid problems associated with ESD.
By dissipating any static charge that may have accumulated on your body, these gadgets shield the diode from harm.
2. Power off
The next safety precaution is power off means when you are handling or connecting a diode in the circuit turn off the power supply.
If the power is left on while connecting the diode to the circuit, you risk receiving an electric shock or spark, which could result in an accident or damage to the other components.
Always ensure that the power is turned off before handling or connecting diodes. This prevents accidental electrical shock and protects the diode from excessive current or voltage.
3. Soldering protection
When soldering the diode in the circuit, keeping some in mind is necessary. As all the electronic components are heat sensitive same is true with the diode.
Diodes are sensitive to high temperatures during soldering, which can damage or affect their performance. Rapid heating and cooling cycles during soldering can cause thermal stress on the diode.
Implementing appropriate precautions such as using heat sinks, and temperature-controlled soldering irons can minimize the risk of diode failure.
4. Heat dissipation
Diodes can generate heat during operation, especially when handling high currents. To handle such head generation, a proper heat management system is necessary.
Ensure that the diode is mounted on an appropriate heat sink if necessary, and avoid excessive power dissipation that could lead to overheating.
This will help to prevent damage to the diode and surrounding components.
5. Polarity check
The next safety measurement is the polarity check of the diode. Double-check the polarity of the diode before connecting it to the circuit.
Connecting a diode with the wrong polarity can result in incorrect operation or even damage.
6. Component rating
Understanding component rating is also considered a safety precaution. If we apply the voltage and current across the diode above the recommended level it will cause the diode to burst out and lead to complete failure.
It is essential to study and understand the diode rating and select the diode that is suitable for your application. Always use diodes that are rated for the voltage and current levels of your circuit.
Conclusion
The diode is commonly used in various electronic circuits for rectification, signal demodulation, voltage regulation, and switching applications.
The proper use and connection of a diode are crucial for its right and reliable functionality. Understanding the rating and identifying the polarity is essential for diode proper usage.
But the question is how to use a diode properly?
It’s always recommended to consult the diode’s datasheet or seek expert advice when designing circuits involving diodes to ensure optimal performance.
Working with a diode requires some safety precautions such as ESD and soldering protection, a proper mechanism for heat dissipation, and an understanding of diode rating.
By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of damage, injury, or accidents when working with diodes and ensure a safe working environment.
This is was all about how to use a diode in a circuit. I hope this article will be useful , when you begin working with diodes,
Thank you and stay blessed…
Other useful posts:
