How to use LED properly (Safety Measurements, 2025)
The proper use and taking safety measurements while working with LED is essential for its reliable and long-span operation.
Understand the LED ratings like forward voltage and current, reverse voltage, and power dissipation before selecting it. This will help you in choosing the right LED for your application and will prevent any accidental damage due to a sudden increase in current. Efficient use of LEDs also requires safety measurements that ensure the longevity of LEDs, prevent electrical hazards, and safeguard individuals working with them.
In this article, we’ll talk about how to use LED properly.
LED proper usage
LED stands for light-emitting diode and it is the electronic component that emits light when the electrical signal is applied across it.
LED is a polarized component so it has positive and negative terminals and it should be connected in the correct orientation for proper functionality.
To use LEDs properly, there are several factors to consider, including electrical requirements, heat management, and appropriate circuit design.
Let’s see step by step how to use an LED properly.
1. LED selection
Selecting an appropriate LED is crucial for better performance of the circuit. You have to understand the project you are working on in terms of applied voltage and current.
The LED needs a specific forward voltage to light up. If the applied voltage is less than the recommended forward voltage the LED will not work.
LEDs require a specific current to produce the desired brightness. Exceeding the maximum current rating can lead to overheating and premature failure.
For example, you choose an LED and the applied voltage is less than its forward voltage and current limits. The LED will not work in this situation and you will be thinking that LED is damaged.
In short, select the LED whose rating is matched with your project requirements.
2. Power supply
For an LED to work or light up properly you have to apply the right amount of voltage across it and for this, you’ll need a power supply.
Ensure that the power supply voltage matches or exceeds the LED’s forward voltage rating. Using a voltage source lower than the forward voltage will result in a dim or non-functioning LED.
3. Limiting resistor selection
Now the next step is to choose a limiting resistor. If the applied voltage and current are high and there is a situation where the LED can be damaged, we have to connect a limiting resistor to limit the current.
To prevent the LED from drawing too much current and burning out, connect a current-limiting resistor in series with the LED. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm’s Law.
To calculate the value of the limiting resistor you can use the formula
R=V-Vf/If
Where R is for resistance, Vf is the forward voltage of LED, V is the applied voltage, and If is the forward current of LED.
4. Polarity
LED is a polarized component so it needs to connect in the correct orientation to perform properly.
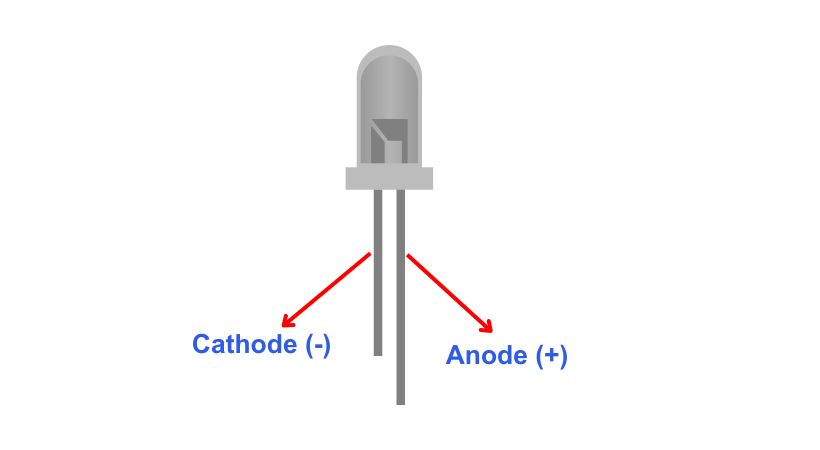
LEDs have two leads – an anode (+) and a cathode (-). The anode is typically the longer lead, and the cathode is the shorter lead. Some LEDs may also have a flat edge or a notch on the body indicating the cathode side.
Identify positive and negative terminals of the LED before making any connection.
5. Connection
It’s time to connect the LED in the circuit. Now connect one end of the limiting resistor to the anode (positive) terminal of the LED and the other end of the resistor to the positive terminal of the battery.
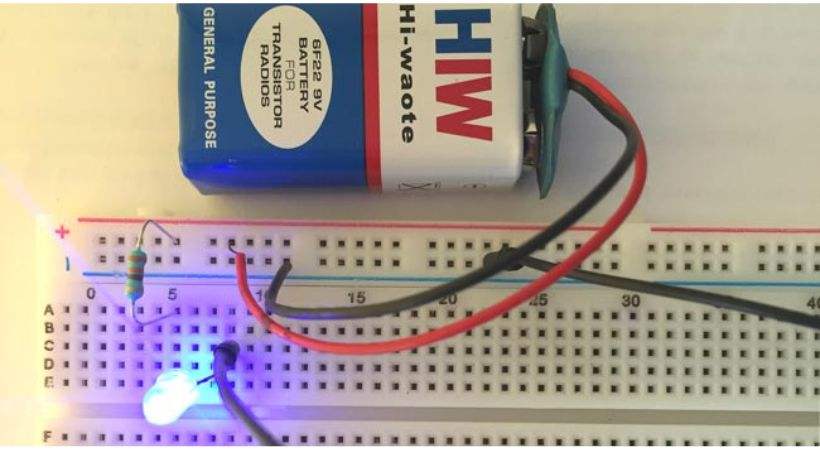

Above is the simple LED circuit.
Connect the cathode (negative) terminal of the LED to the negative terminal of the battery. These connections are for simple LED circuits.
The connection of LED also depends upon the circuit schematic you are working on.
6. Test and troubleshoot
Once the LED is properly connected to the circuit, power it up and observe if it lights up as expected.
If the LED does not light up, double-check the polarity and connections. Verify that the power supply voltage is within the LED’s operating range.
Also, ensure that the current-limiting resistor is the correct value and properly connected.
Safety measurements
Working with LEDs, like any electronic component, requires certain safety measures to ensure personal safety and prevent damage to the components.
Here are some safety considerations when working with LEDs:
1. Adhere to specifications
The LEDs have specific limitations or ratings that define their operation specification. LEDs have specific voltage and current requirements.
Exceeding these limits can damage the LED or pose a safety risk.
Always refer to the datasheet or specifications provided by the LED manufacturer and use the appropriate resistors or driver circuits to ensure proper operating conditions.
2. Avoid overheating
Since LEDs are heat-sensitive, too much heat can shorten their lifespan or cause them to malfunction.
During soldering, if you apply too much heat while making a connection it will also damage the LED
When designing LED applications, make sure that there is sufficient ventilation or the use of heat sinks to provide proper heat dissipation.
3. Polarity check
Double check the polarity of the LED while connecting it because wrong polarity connections will lead to malfunction of the LED.
The longer lead is typically the positive (anode), and the shorter lead is the negative (cathode). To avoid the risk of damage try to connect the LED in the right orientation.
4. Avoid overloading
Make sure you don’t overload the circuit, which means don’t connect too many LEDs in the circuit.
Connecting too many LEDs will lead to high power dissipation and will cause failure of the component. Proper heat management is necessary in this case.
5. Mechanical safety
LEDs are delicate electronic devices and can be easily damaged by physical stress or impact. Handle them gently and avoid applying excessive force or pressure.
Use appropriate tools, such as tweezers or specialized LED handling tools, to manipulate LEDs without causing damage.
Protect LEDs from mechanical stress or vibration during installation and use.
Conclusion
Light-emitting diodes, or LEDs, are energy-efficient and adaptable light sources that can be utilized in various applications, including electrical devices, displays, lighting fixtures, and indications.
The understanding of proper usage and safety measures is essential for its correct and reliable operation.
Proper usage of LEDs involves understanding the electrical requirements and the right selection, identifying the polarity, choosing the correct limiting resistor, and designing appropriate circuits.
Always prioritize safety while working with LED. Try to adhere to LED specifications, avoid overheating and overloading, and double-check the polarity.
Remember, these safety measures are general guidelines, and specific safety requirements may vary depending on the type of LED.
This was all about the safety precautions of the LED, I hope you’ll learn a lot from this article.
Thank you and stay blessed…
Other useful posts:
