Welcome to the fascinating world of electronics, where even the smallest components have tremendous power. The capacitor is the hero of the circuit board, which plays a vital role in the shaping and functionality of electronic devices.
Capacitors come in various shapes and colors; some resemble buttons, while others are shaped like small tubes. They often have strange numbers and letters written on them, which indicate how much energy they can store. These small components are strategically placed all over the circuit board. By understanding their structure, you can easily identify capacitors on the circuit board.
This article is here to help you understand and identify a capacitor, even if you’re just starting in electronics.
Identification of capacitor in circuit board
In electrical circuits, capacitors are often used for a variety of functions including filtering, coupling, energy storage, and timing.

To learn about capacitor function check the article
In addition to numerous other electrical devices, power supplies, audio circuits, and radio receivers all contain them.
Capacitor has different types and construction such as electrolytic capacitors and ceramic capacitors. Each has its characteristics and functionality.
To identify capacitors in circuit boards, here are some key factors that should be considered.
1. Understand capacitor markings
Most capacitors have markings on their bodies that provide important information about their specifications. The most common markings found on capacitors include the capacitance value, voltage rating, and tolerance.
The capacitance value is the most crucial parameter of a capacitor. It defines how much energy a capacitor can store.
Capacitance is measured in Farads (F), but in practice, capacitors have much smaller values, so they are typically expressed in smaller units such as microfarads (μF), nanofarads (nF), or picofarads (pF).
A capacitor may have a value like “10” or “47” indicating a capacitance of 10 μF or 47 μF, respectively. On some capacitors, the maximum operating voltage and tolerance are also mentioned.
We also have a detailed article on: How to read capacitor values
The maximum voltage is printed on a capacitor like 16V or 50V. A capacitor might have a tolerance marking like “±10%,” indicating that the actual capacitance can deviate by up to 10% from the stated value.
It’s crucial to remember that not all capacitors have the three markings (voltage rating, tolerance, and capacitance value) printed on them.
Certain capacitors may have shortened or manufacturer-specific marks, especially the small surface-mount types.
2. Physical characteristics
The different types of capacitors have different physical characteristics. By understanding these you can easily find the capacitor.
There are two types of capacitors, electrolytic capacitors and ceramic capacitors.
Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors are commonly polarized capacitors, which means they have a positive and negative terminal.
The electrolytic capacitors are typically cylindrical in shape. They can have axial or radial leads. If the leads are extended from both ends, the leads are axial, and the leads extended from one side are radial.
These capacitors also have a “+” symbol to indicate a positive terminal and a “-” symbol to show a negative terminal.
Ceramic Capacitors
The ceramic capacitors are non-polarized ones which means any of the terminals can be taken positive and negative.
They have different shapes including rectangular, square, or disc-shaped. Their sizes vary from small surface mount components to large through-hole components.
This type of capacitor has alphanumeric codes printed on their bodies, indicating the capacitance value. With the help of these physical characteristics, you can easily identify the capacitor in the circuit board.
Location on circuit board
Have you ever wondered where on a circuit board these little components known as capacitors are hidden? They’re scattered all around, and each has a specific job to help the device work properly.
Capacitors are frequently located close to locations where electricity enters or exits a device. They act as sort of gatekeepers, ensuring that the electricity runs smoothly and doesn’t cause any problems.
Capacitors can also be found near special parts of the circuit board, such as the part that handles the sound or the screen. It also teams up with other parts to help signal to travel smoothly through the device.
Understanding the location of these capacitors can help in our understanding of the device’s operation. Every location they occupy serves a certain function, and their presence ensures that everything goes without any problems.
Identifying capacitor visually
Have you seen those small parts that look like buttons or tiny cylinders on a circuit board? Those are capacitors! They come in different shapes, colors, and sizes.
Let’s identify the different capacitors in the circuit board by using the above information.
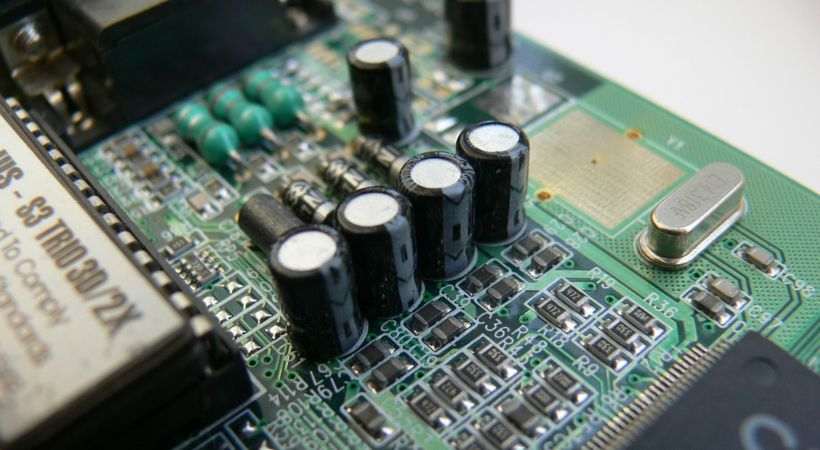

As you can see we have cylindrical shape components in the above circuit board. On these components, the voltage and capacitance values in Farad (F) are also mentioned. This means that these components are capacitors.
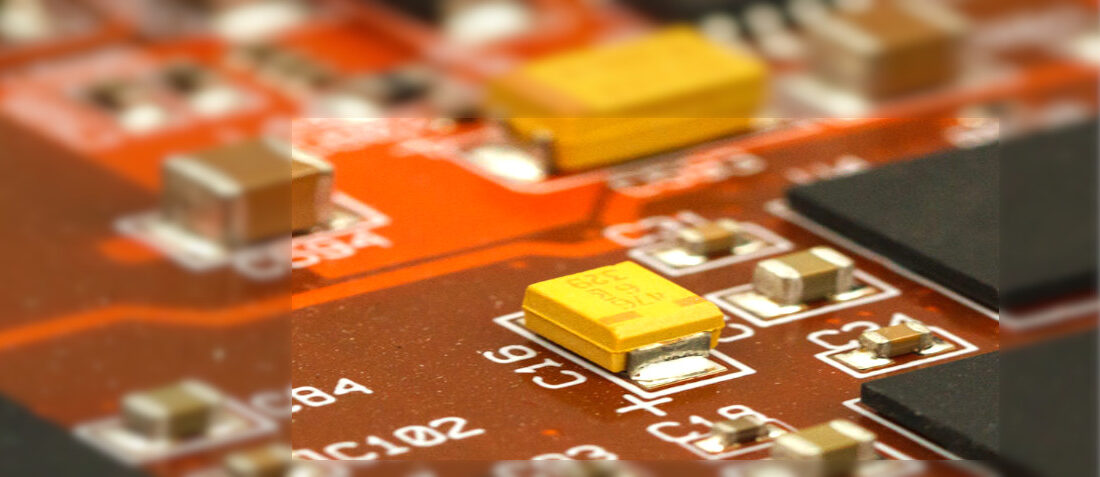
Now some capacitors are rectangular in shape. In the above circuit board, you can see there are some components that have rectangular shapes and the circuit also defines this part as ‘C1’, ‘C2’, and so on.
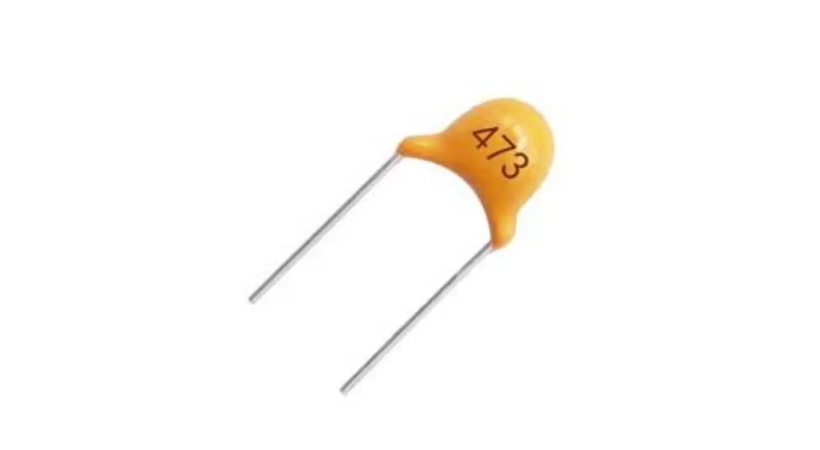

As we know ceramic capacitors have some code written on them to define their capacitance. So above the component capacitor, its maximum voltage and capacitance code are mentioned.
Knowing these different looks helps you recognize capacitors on a circuit board.
Safety considerations
It is always advised that when working with capacitors consider some safety precautions. The capacitor stores electrical energy even when disconnected. Here’s how to stay safe while learning about these little electronic helpers:
1. Discharge the capacitor
Make sure all capacitors on a circuit board are discharged before handling or working on them. This means removing any stored electrical charge.
If the capacitor is not discharged properly and you start working with it, this will give you an electrical shock.
The discharging can be accomplished by carefully draining the electricity from them using a resistor or other specialized instrument.
2. Be mindful of the voltage ratings
Various voltage levels can be stored by capacitors. Make sure you’re not working with a capacitor that can handle a voltage higher than what you are ready for by checking frequently.
You could receive a painful shock from high-voltage capacitors.
Always understand the voltage ratings of the capacitor to avoid any accidental injury and component damage.
3. Avoid short circuits
Sometimes when working with a capacitor you can accidentally connect the ends of a capacitor with each other.
When testing capacitors or working on a circuit board, make sure you don’t accidentally create a short circuit. This can cause sparks or damage to the components.
Practical Tips
Here are some practical tips for identifying capacitors on a circuit board in simpler terms:
- Use a magnifying glass or zoom in on your phone’s camera to get a better view. Sometimes, these little parts have tiny numbers or letters that can be hard to see with just your eyes.
- Capacitors come in different shapes and sizes. Some are circular and flat, while others resemble little cylinders. You can identify these shapes more quickly if you are familiar with them.
- Often, capacitors of the same type are placed in groups on the circuit board. They might look similar and sit close to each other.
- You will get better the more circuit boards you examine. It may seem a little difficult at first, but with practice, it becomes simpler.
Remember, the key is to take your time and not rush.
Fun activity: Identify a capacitor in the circuit
Now you have learned how can you identify a capacitor in the circuit. It’s time to find capacitors using the above information.
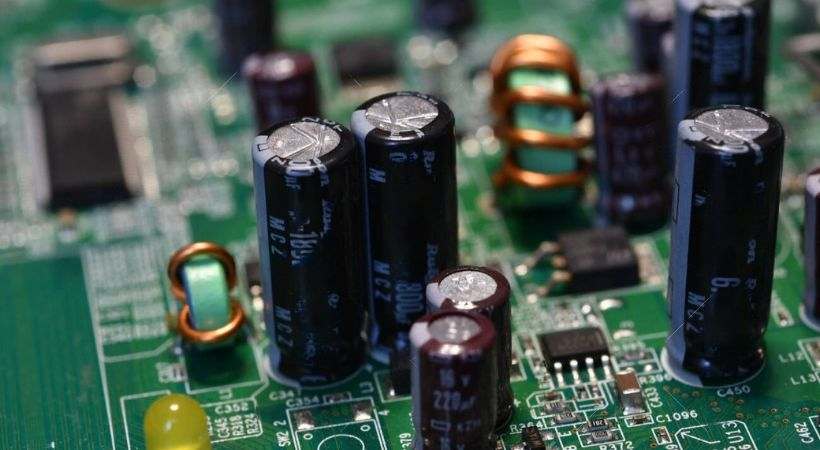

Identify how many capacitors are present in the above circuit and write it down in the comment section.
Conclusion
A capacitor is an electronic components that store electrical energy. They are not only necessary for the storage and release of electrical energy, but they also play a role in signal filtering, power quality, and system efficiency.
Identifying capacitors on a circuit board may seem challenging, some several key steps and techniques can simplify the process.
The first thing is understanding the physical characteristics of the different capacitors. Second, you may learn a lot by looking at the marks on the capacitor itself.
The capacitance value, voltage rating, and tolerance of capacitors can be represented by numerical values, letter codes, or alphanumeric codes.
You can quickly become an expert at identifying and comprehending capacitors on circuit boards with a little practice and these useful steps.
This was all about the process of identifying a capacitor in a circuit, I hope this helps you in the finding process.
Thank you and stay blessed…
Other useful posts:
