LEDs come in different types with different specifications and ratings which give us information about their electrical characteristics.
Understanding LED ratings is crucial when selecting and working with one. You will prevent damage and will ensure safety by providing appropriate voltage and current to the LED. All this is possible by knowing the LED ratings such as forward voltage and current, reverse voltage, wavelength, luminous intensity, power dissipation, and operating temperature. By carefully considering and adhering to these ratings, you can harness the full potential of LEDs.
In this article, Let’s discuss the LED ratings for better selection and performance.
LED ratings
An LED rating refers to the specified electrical and optical parameters that determine its performance and safe operation.
Different ratings and criteria are attached to LEDs, which tell you about their optical and electrical properties. When choosing and using LEDs, it is essential to understand these ratings.
Typical LED ratings are as follows:
1. Forward current
The forward current is a crucial parameter which means the maximum current an LED can handle when it is forward-biased.
The forward current rating, usually measured in milliamperes (mA), represents the maximum current that the LED can bear.
Exceeding the current limit will affect the LED performance and can lead to potential damage to the circuit and other components. When working with LED, make sure it operates within the forward current limit.
Select the LED that has a forward current limit matching your circuit-applied current.
2. Forward voltage
The forward voltage is the voltage required to turn the LED on and allow current to flow through it.
It is a crucial parameter to ensure the proper operation of the LED. Different LED colors and types have different forward voltage requirements.
If the applied voltage is less than the LED forward voltage the LED will not work and exceeding the limit can lead to overheating and permanent damage.
Forward voltage for different LEDs varies from 1.8 to 2.2V. You carefully match applied voltage values to the LED’s specifications to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
3. LED wavelength
The LED wavelength rating is a critical parameter that defines the color of light emitted by the LED. Wavelength is usually measured in nanometers (nm).
Different colors of LEDs have different wavelengths. Red LEDs typically have longer wavelengths, around 620-750 nm, while blue LEDs have shorter wavelengths, ranging from 450 to 495 nm.
Green LEDs fall in between, with wavelengths around 495 to 520 nm. The wavelength rating is a key factor in determining the aesthetic appeal and functionality of LED-based products.
Consider this factor during the design and selection phase.
4. Luminous intensity
One of the most important factors in assessing and comprehending LED performance is luminance.
It is measured in candelas (cd) and describes the amount of visible light emitted by an LED in a certain direction. The LED brightness and concentration of light in the specific direction are defined by luminous intensity rating.
The luminous intensity of different LEDs varies from 150 to 200mcd. The higher the luminous value, the more contented light will be emitted by LED in a specific direction.
This rating is particularly important in applications where directional lighting is crucial, such as in flashlights, spotlights, or automotive headlights.
5. Power dissipation
Power dissipation (Pd) is the amount of power the LED can handle without being damaged.
It is the product of forward voltage and forward current (Pd = Vf * If) and it is measured in milliwatts (mW).
Exceeding the maximum power dissipation can lead to thermal issues, affecting efficiency and reliability.
Proper thermal management is crucial, and understanding power dissipation helps in designing circuits that dissipate heat effectively.
6. Reverse voltage
LEDs are designed to operate in the forward direction. Applying a reverse voltage can cause damage.
The reverse voltage (Vr) rating indicates the maximum voltage that can be applied in the reverse direction without harming the LED.
Incorporating protective measures in circuits, such as diodes or reverse voltage protection devices, is essential to prevent accidental reverse biasing.
Take the reverse voltage rating into account for better performance for LED.
There are the ratings of LED that define its operational conditions. All information related to LED parameters is provided by manufacturers in the datasheet.
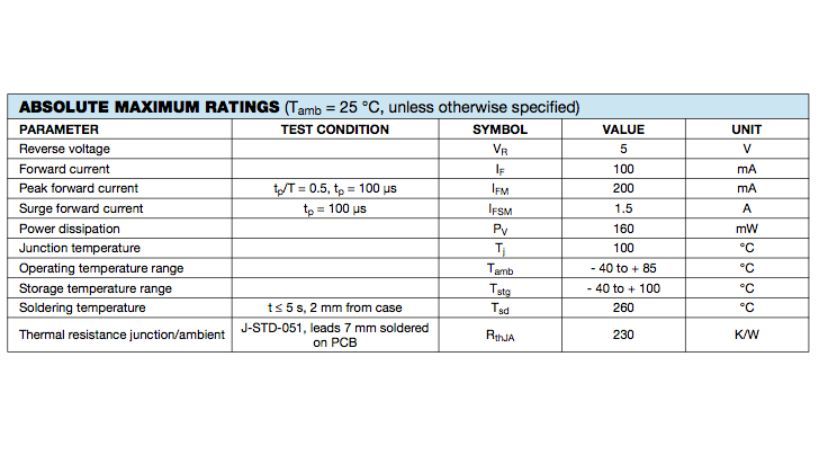
Here is an example of an LED datasheet, where all electrical parameter values are defined.
Importance of LED ratings
Understanding LED ratings is crucial for several reasons: it guarantees appropriate handling, reliable operation, and extended lifespan of the LED in different applications.
Here is a detailed explanation of why understanding LED ratings is essential.
1. Preventing damage
Studying and learning the ratings of LED will prevent damage to the LED and other components in the circuit. LED has specific ratings, such as forward voltage (Vf), forward current (If), power dissipation (Pd), and others.
If these limits are crossed, the LED will burn and get damaged, which will result in a permanent failure of the circuit. For example, if you exceed the forward current and voltage level it will increase power dissipation.
The increased power dissipation, causes the LED to overheat and potentially fail. When you choose the LED keep the different ratings in mind.
2. Optimizing performance
The knowledge of ratings also optimized the performance. The forward voltage indicates the voltage at which the LED operates efficiently, and the forward current specifies the optimal current for proper functioning.
These values must be considered in conjunction to avoid overdriving the LED, which can result in overheating and premature failure.
By selecting LEDs with appropriate ratings and understanding their interdependencies, designers can create circuits that operate efficiently, delivering the desired brightness and color while avoiding stress on the LED.
3. Prevent overheating
Preventing overheating ensures the longevity of LED-based systems. Properly handling the current, voltage, and power dissipation will damage the LED.
Exceeding forward current and voltage values can lead to increased power dissipation, generating excess heat that can damage the LED. If you know LED ratings you will handle it well.
To implement proper thermal management strategies, prevent overheating, and create reliable LED systems in various applications LED rating is essential.
4. Ensuring safety
To guarantee safety in electrical circuits and lighting systems, it is essential to understand LED ratings.
Similar to any other electronic component, LEDs have certain operating limits that, if beyond, can cause deterioration, overheating, and even failure.
By carefully considering parameters such as forward voltage, forward current, and power dissipation, one can design circuits that operate within the manufacturer-specified limits.
Conclusion
For the safe and reliable operation of LED, understanding its rating is crucial. LED is the electronic component that emits light when voltage is applied across it.
It is used in various applications like optical communication, backlighting, decorative lighting, and as an indicator for power, flashlight, and status.
The LED rating provides information about their electrical and optical characteristics. It includes
- Forward current
- Forward voltage
- LED wavelength
- Luminous intensity
- Power dissipation
- Reverse voltage
Understanding these ratings is essential for selecting the right LED for a specific application, designing circuits that operate within safe limits, and ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
Rating will help in
- Preventing component damage
- Optimizing performance
- Avoiding overheating
- Ensuring safety
Understand these ratings for better selection and reliable, and smooth operation of LED in the circuit.
This was all about the LED rating, I hope you like it.
Thank you and stay blessed…
Other useful posts:
