Ohm’s law is the most important and basic in electronics. This law describes the fundamental relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in electrical or electronic circuits.
When the voltage is applied across the conductor the current is produced due to the movement of charges, ohm’s law states that this current is directly proportional to the applied voltage as long as the temperature is constant. The ohm’s law has its applications, and its significance in the world of electronic circuits.
If you’re a student just beginning to study electronics, you must have a solid understanding of Ohm’s Law.
In this article, you’ll learn everything about Ohm’s law, its mathematical form, and the different variations of its formula.
Ohm’s law
Ohm’s law is the basic principle in electrical and electronics engineering and physics that describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
Ohm’s Law is a simple and widely applicable principle that helps understand and predict electrical and electronic circuits‘ behavior.
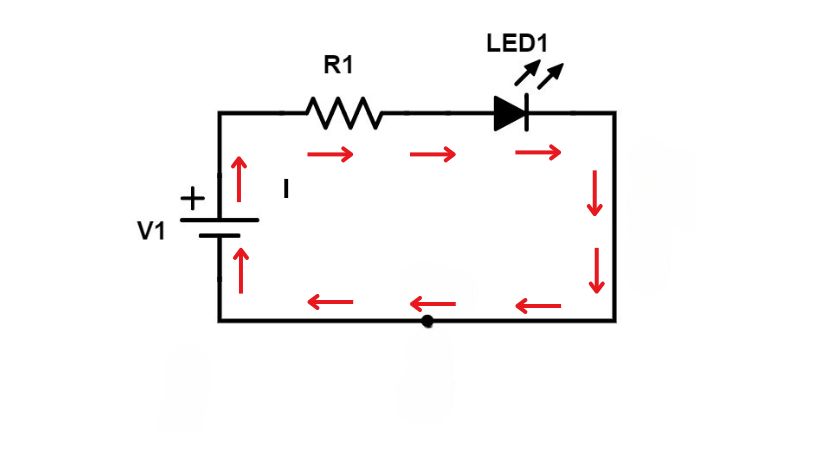
Ohm’s law states that
“The current (I) flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the two points as long as the temperature and the physical state of the conductor are kept constant.”
It means if the voltage becomes double the current across the conductor also becomes double.
Mathematically, Ohm’s law can be represented as
V ∝ I
Here ‘V’ represents voltage and ‘I’ represents current.
V=RI
Where ‘R’ is called resistance and Its value depends upon the nature of the material and the dimension of the material such as cross-sectional area and length.
Let’s understand Ohm’s law using the water analogy. For example, we have a water tank and a pipe attached to it.
In this, the water pressure is voltage, the water flowing from the pipe is current and the resistance is the size of the pipe. Now if the pressure of water is high, the bigger is pipe size (low resistance) more water will flow.
So same is true for Ohm’s law: the voltage is high and the lower the resistance more current will flow in a circuit.
It’s needed to add that all the devices don’t obey Ohm’s law such type of devices is called non-ohmic devices. The type of devices that obey Ohm’s law are called ohmic devices.
1. Ohmic devices
The ohmic devices are those devices that obey Ohm’s law. The resistor and wires are the two examples of ohmic devices. Let’s explain these with the help of its voltage-current graph.
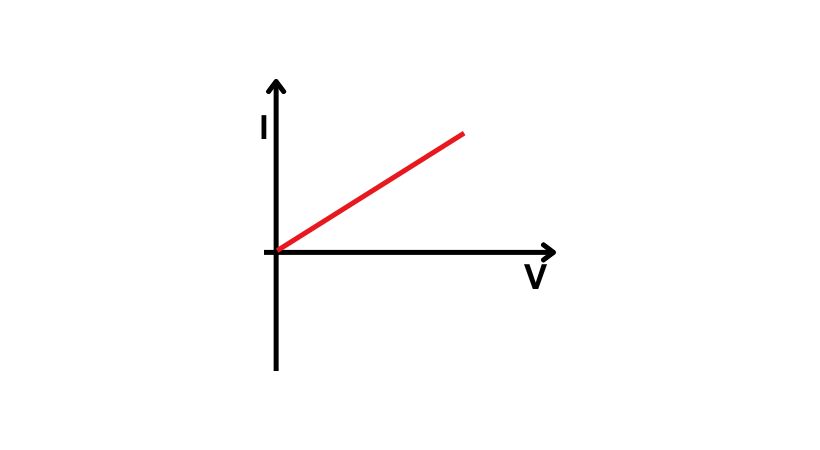
From the above graph, we can see that by increasing voltage there is an increase in the current so the line is straight. It means the ohmic devices will have a straight line when their voltage-current graph is plotted.
2. Non-ohmic devices
The devices that don’t follow Ohm’s law are known as non-ohmic devices. Vacuum tubes and thermistors are two examples.
The voltage-current graph of non-ohmic devices is not a straight line which means with an increase in the voltage the current does not increase.
As the graph shows at the start, the voltage is increasing but there is no current and after some time when the voltage reaches a specific limit the current starts increasing.
Understand resistance
It is essential to study the resistance to understand Ohm’s law fully. The opposition offered to the flow of current is called resistance.
As we know the charges are transmitted by free electrons. The resistance is due to the collision of free electrons in the conductor. The resistance in the circuit can be measured using Ohm’s law,
R=V/I
So from this, the SI unit of resistance is Ohm and can be represented by the Greek letter omega (Ω).
The resistance of a wire can be 1Ω if a voltage of 1V is applied across the ends and causes a current of 1A to flow through it.
The devices that offer resistance to the current flow are known as resistors. The resistors have a wide range of values. It can vary from kilo to mega ohm depending upon the application.
Triangle technique of Ohm’s law
When examining electronic circuits, Ohm’s Law is a highly helpful and basic tool. It must be committed to memory by students because it is utilized so frequently in the study of electronics and electricity.
So here is the trick that will help you to memorize Ohm’s law. This trick is the triangle technique. Let’s see this technique in detail.
The first step is to arrange the voltage, current, and resistance in the triangle.
If the values of voltage (V) and current (I) are given and want to find resistance (R). So just remove the R from its place.
Now if you want to find ‘I’ then eliminate the I from its place and see what is left.
Finally, if you are aware of I and R and want to find V, take out V and observe what remains:
This a simple trick that will be very useful while you are solving electronic circuits.
Simple circuit with Ohm’s law
Let’s see how Ohm’s law helps us to understand simple circuits and find the unknowns.
In the above circuit, we have one voltage source on the left and only one source of resistance to the current on the right side.
Here applying Ohm’s law is very easy. You can find the third one using Ohm’s law if you know any two among voltage, current, and resistance.
In the first example, we will calculate current (I), by using values of voltage (V) and resistor (R).
How much current will be flowing in the above circuit?
We know
V=IR
I=V/R
Now we know V = 9V and R = 5Ω.
I=9V/5Ω
I=1.8A
This is just a simple example of how Ohm’s law is used to find unknowns in the circuit.
You use the current value from the above example to find the voltage and resistance of the same circuit to see if the calculated current value is correct or not.
Limitations of Ohm’s law
There are some limitations of Ohm’s law. The limitations of Ohm’s law are the following.
- Since some electronic components like diodes and transistors only permit current to flow in one way, Ohm’s law does not apply to them.
- It is challenging to apply Ohm’s law to non-linear electrical elements since their voltage-to-current ratio will not be constant over time due to characteristics like capacitance, resistance, etc.
- Ohm’s law only applies to conductors made of metal. Thus, in the case of non-metallic conductors, it will not function.
Applications of Ohm’s law
The key applications of Ohm’s law are:
- In an electric circuit, it helps to find voltage, current, and resistance.
- Ohm’s law helps to maintain the desired voltage drop across the electronic components.
- It also helps in finding the power consumption of various appliances.
- We can calculate the maximum amount of current that could pass through the fuses using Ohm’s law. An excessive current value has the potential to destroy the circuit and perhaps cause the electrical devices to explode.
Ohm’s law is one of the bases to get started with electronic basics. It allows you to find the current flowing in each component if the voltage and resistance are known and many more.
Take your time to understand it thoroughly.
Conclusion
Ohm’s law is the basic law in the field of electronics and electrical engineering. It helps to solve different circuits and find the value of voltage, current, and resistor.
Ohm’s law describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistor. It is stated that the applied voltage across the conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through the conductor.
The devices that obey Ohm’s law are known as ohmic devices and those that don’t obey are called non-ohmic. The voltage-current graph of ohmic devices is a straight line.
For unilateral components, ohm’s law can not be used. The unilateral components are diodes and transistors. Ohm’s law is only applicable to metallic conductors.
To find the values of voltage, current and resistor ohm’s law can be used. To maintain and control the power consumption of different appliances ohm’s law is helpful.
This was all about Ohm’s law, after learning it you will be able to find different parameters in the circuits.
Thank you and stay connected to our website.
Other useful posts:

TKS. very good