Ohm’s law using multimeter (Verification, 2025)
Verifying Ohm’s law using multimeter experimentally is crucial for understanding its practical implications in circuit analysis and design.
A multimeter or multi-function device can be used to verify Ohm’s law. The resistor with a fixed resistance, a power source, connecting wires, and a digital multimeter are all you need for verification. Connect one end of the resistor to the positive of the power source and the other end to the negative. Increasing the voltage across the resistor will also increase the current. You can measure the current across the resistor by connecting the multimeter in series with the resistor.
In this article, we’ll examine how Ohm’s law will be verified using a multimeter.
Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s law is one of the basic laws of electrical and electronic engineering, which describes the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance.
It is named after the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm, who first formulated this law in the 19th century.
Ohm’s law states that the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it by keeping the resistance of the resistor constant.
Mathematically, Ohm’s Law is expressed by the equation:
V=I×R
Where:
- “V” is the voltage across the component or circuit (measured in volts, V).
- “I” is the current flowing through the component or circuit (measured in amperes, A).
- “R” is the resistance of the component or circuit (measured in ohms, Ω).
This law can be verified by using a multimeter. Let’s discuss the procedure you can use to verify the ohm’s law.
Ohm’s law using multimeter
A multimeter is a versatile electronic measuring instrument used to measure various electrical quantities in circuits.

It combines multiple measurement functions into a single device, typically including voltage, current, and resistance.
The multimeter is available in both digital and analog formats, but nowadays digital multimeter is more common because of its easy-to-use design.
This tool can be used to verify the ohm’s law. Before delving into the experimental procedure, it’s imperative to gather the necessary equipment:
1. Components needed
Here is the list of the components you will need for verification of Ohm’s law.
Multimeter: Choose a suitable multimeter capable of measuring voltage (volts), current (amperes), and resistance (ohms). Digital multimeters are preferred for their precision and ease of use.
Resistors: The resistors are needed to serve as the components in the circuit whose behavior we aim to analyze. Make sure you know the resistors’ values.
Power Source: Secure a reliable power source, such as batteries or a variable power supply, to energize the circuit. A variable power supply will be good to change the voltage and analyze Ohm’s law more efficiently.
Connecting Wires: The insulated connecting wires will be needed to establish electrical connections between the components in the circuit.
Breadboard: It provides the platform to connect the resistor to the power source for the measurements.
2. Circuit connection
Take a breadboard, and insert the resistor on the breadboard. Make sure the leads of the resistor are inserted correctly.
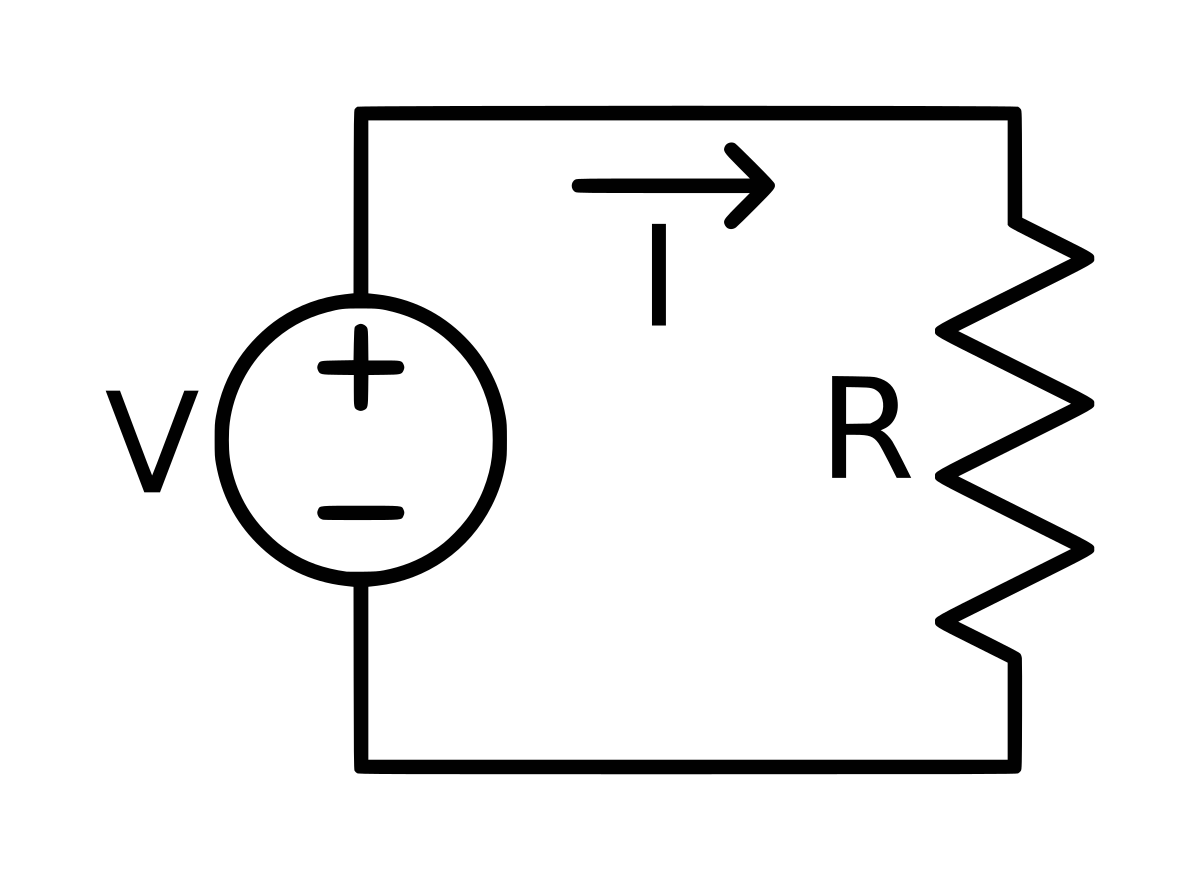
Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to one end of the resistor and the negative terminal to the other end of the resistor.
3. Setting up the multimeter
Now it’s time to set up the multimeter for measurement. Follow the following steps to set up a multimeter.
- Turn on the multimeter.
- Insert the probes of the multimeter, the black probe in the COM, and the red probe into the slot which are designed to measure the parameter you want.
- Select the mode by rotating the selection dial of the multimeter, in our case, we measure current.
- If you are using a manual range multimeter, you have the range of the multimeter.
These are some steps that can be performed to set up a multimeter for further measurements.
4. Experimental procedure
You have already made the connections and set up a multimeter, let’s discuss how can you verify Ohm’s law.
- First, if you don’t know the resistance value of the resistor, select the resistance mode on the multimeter and connect the probes of the meter to the resistor. This multimeter will give you a resistance value.
- After that apply the voltage across the resistor.
- Change the mode of the multimeter from resistance to the ampere, ampere mode is used to measure the current flowing in the circuit.
- Remember that the multimeter should be connected in series with a circuit to measure current.
- Disconnect one end of the resistor from the power source. Set the multimeter to the current (A) measurement mode and connect it in series with the resistor and the power source.
- The current value will be displayed on the screen, note the current value.
- Now slowly start increasing the voltage and measure the current value for different voltages.
- As you increase the voltage, the current will start increasing.
- You can repeat the whole process for different resistors and can see the relationship between voltage and current.
By following these steps you can understand and verify Ohm’s Law using a multimeter. By keeping the value of the resistance constant, the current increases as you increase the voltage.
Tips for the experimental procedure
Here are some additional tips that will help you…
- Ensure that the multimeter and other equipment used in the experiment are calibrated and accurate to obtain reliable results.
- Make the right and secure connections when connecting the components in the circuit.
- Conduct multiple measurements with different resistors and under various conditions to validate the consistency of Ohm’s Law across different scenarios.
- When working with electrical circuits take the safety measurement, such as wearing appropriate protective gear and avoiding contact with live circuits.
Conclusion
In electrical and electronic engineering, Ohm’s law is the most used law that’s why it is considered one of the fundamental laws of engineering.
Ohm’s law states that by keeping the value of the resistor constant, the voltage is directly proportional to the current flowing in the resistor.
As a beginner, you just want to verify if this really happened or not. A digital multimeter is the tool that is used to verify Ohm’s law.
Take a resistor and connect it to the power supply. Select the ampere mode on the multimeter and measure the current flowing in the resistor.
Measure the different values of current by changing the voltage across the resistor. Note all these measured values and you will note that by increasing the voltage the current is also increasing.
Keep in mind that the multimeter should be connected in series across the resistor to measure current.
So this was all about the use of a multimeter for verifying Ohm’s law. I hope after reading this article you’ll confidently perform this experiment.
Thank you and stay blessed…
Other useful posts:
