A resistor is part of every electronic circuit. Whenever you start working with circuits you’ll see resistors in it. Understanding the rating of the resistor is essential for the circuit’s proper functionality.
A resistor rating defines key characteristics like resistance value, power rating, temperature coefficient, and voltage rating, indicating its strengths and limitations. The power rating specifies the maximum energy a resistor can safely dissipate as heat. Proper resistor ratings ensure circuit performance, reliability, and safety by preventing component damage.
This article will discuss the resistor ratings and why it is important.
Resistor ratings understanding
A resistor is a passive two-terminal component that opposes the flow of current. This component is designed in such a way that it controls the amount of current in the circuit.
Understanding the ratings and basics of resistors is crucial because they are a component of all electronic circuits.
What are component ratings? It defines the specifications by which a component can perform safely and effectively.
So the term “resistor ratings” generally refers to the specifications and parameters associated with a resistor that define its characteristics and limitations.
These parameters provide information regarding how the resistor will behave in the circuit and how much power, voltage, and current will be required for it.
The resistors come in various types, shapes, and sizes. They are used in various electronic circuits for voltage division, current limiting, signal controlling, and temperature settings.
Some of the key resistor ratings are the following.
1. Resistance value
It is one of the most fundamental ratings of resistors. The resistance value defines how much resistance or opposition can be offered by a resistor to the flow of current.
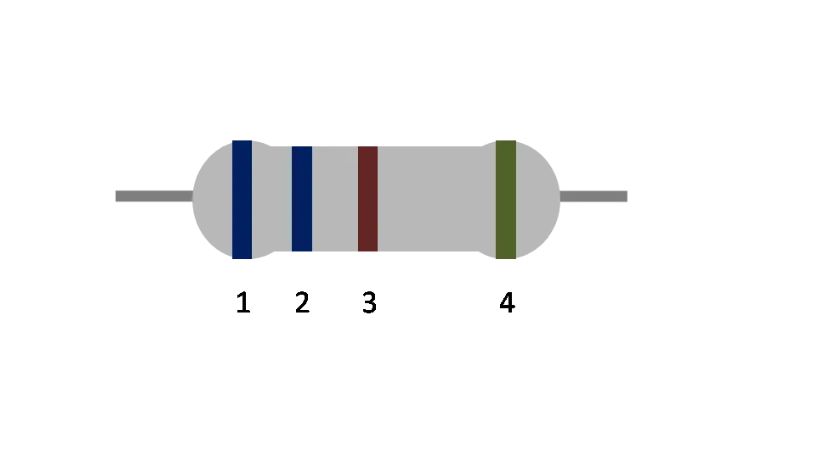
It is measured in ohm (Ω) and it determines the relation between voltage and current in the circuit. The resistance value can be determined through color bands printed on the resistor.
Each band represents a specific number and by identifying these numbers you can find the resistance value.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance specifies how much the actual resistance value can vary from its nominal value. It is expressed as a percentage.
A 100Ω resistor with ±5% tolerance can have a real resistance between 95Ω and 105Ω. Keep this thing also in mind while selecting a resistor for your project.
3. Power rating
The power rating of a resistor specifies the maximum amount of power it can safely dissipate without overheating or getting damaged. It is measured in watts (W).
In general, the maximum power rating is determined by its physical size. If the surface area of the resistor is more than the greater power it can dissipate safely.
In other words, we can also say that power rating shows how much power the resistor can convert into heat or absorb safely without damaging itself.
Depending on its size, structure, and operating temperature, resistors can have power ratings ranging from less than a tenth of a watt to several hundred watts.
It is measured in watts and W is written with it. Like other electrical quantities, the prefix is attached with watts to express the smallest and largest power of the resistor.
For example, milliwatt (mW) and kilowatt (kW). Mathematically different formulas are used to measure the power rating of resistors.
Ohm’s Law tells us that when a current passes through a resistance, a voltage drops across it, and this produces a product that gives us power.
So
Power (P) = Voltage (V) ✕ Current (I)
P=VI ………..(1)
From Ohm’s Law, the voltage is equal to the product of current and resistance. So the above equation will become.
P=IR(I)
P=I^2R …………(2)
Ohm’s law also tells us about the current which is equal to
I=V/R
So the power equation becomes
P=V(V/R)
P=V^2/R ……….(3)
These three equations can be used to find the power dissipation of any resistor in the D.C. circuit.
Overloading a resistor can cause heat stress and resistor failure. It is essential to select a resistor whose power rating is greater than the circuit’s expected power dissipation.
4. Temperature coefficient
Temperature coefficient defines the change in resistance with respect to temperature.
Certain resistors exhibit more stability in the presence of temperature variations, whilst others undergo substantial resistance changes. It is usually expressed in parts per million per degree Celsius (ppm/°C).
If the resistance increases with an increase in temperature it is called a positive temperature coefficient and if resistance decreases with an increase in temperature is called a negative temperature coefficient.
5. Voltage rating
The voltage rating means how much voltage a resistor can safely sustain without damaging itself. In high-voltage applications, we will always look for resistors that have high-voltage ratings.
Exceeding the voltage rating can cause arcing or damage to the resistor and the circuit. It is crucial to select resistors with voltage ratings suitable for the specific application.
Resistor rating importance
There are various reasons why resistor ratings are important. Let’s examine in more detail why resistor ratings are important in electronic circuits and why you should understand them.
1. Selection of the right resistor
Most importantly, rating helps us in selecting appropriate resistors for our application or project. By understanding different ratings of resistors, you can select a resistor that is suitable for your project.
Resistance value, power rating, tolerance, temperature coefficient, and voltage rating of a resistor should be considered when looking for various resistors.
2. Preventing resistor failure
Resistors have limitations on the amount of power they can safely dissipate. Overloading the resistor can result in overheating, which can alter its resistance value, reduce its performance, or possibly cause it to fail.
You can reduce the chance of resistor failure by choosing a resistor that can withstand the expected power dissipation in your circuit by taking the power rating into account.
3. Accuracy and precision
By considering the rating of the resistor, the accuracy and precision of the circuit performance increases.
By understanding the resistor ratings, you can choose resistors that meet the desired level of precision for your application.
4. Temperature consideration
The temperature coefficient of a resistor helps to understand the behaviors of a resistor with temperature change. Various resistor has different temperature coefficients.
You may predict and account for variations in resistance brought on by fluctuations in temperature by taking the temperature coefficient into account.
This is especially crucial in applications where temperature changes can have a big impact on the functionality of the circuit.
5. Safety
Resistor ratings plays a crucial in the safety. If you pick a resistor without looking at its rating. The resistor will be harmed or it may catch fire and cause damage if you apply voltage above what is recommended.
Understanding the recommended ratings reduces the possibility of overheating, failure, or other potential dangers by ensuring that the resistors function within their limitations.
Conclusion
A Resistor is a fundamental component of an electronic circuit, it is used to control the flow of current in the circuit.
When selecting a resistor for your project it is essential to understand its ratings. The resistor ratings are a set of specifications or characteristics of a resistor that define its behavior.
The resistance value, power rating, temperature coefficient, and voltage rating are key parameters to consider. The power rating defines how much energy can a resistor dissipate or sustain without damaging itself.
One can select the ideal resistor for a given circuit and ensure safe and dependable operation by paying attention to these ratings.
That is all about resistor ratings, I hope it will clear your confusion regarding the rating of resistors.
Thank you and stay blessed…
**We learned about resistor ratings. You can continue your resistor learning by checking out the resistor function and its key role in real electronic circuits.
