Electricity is an invisible force that powers nearly every aspect of modern life. An electronic circuit needs electricity to function.
But what is electricity?
Electricity is the phenomenon of the flow of electric charges in a complete circuit—thus allowing the circuit or device to power up and work properly. The electric charges are mostly free electrons. These free electrons move from the negative terminal of a voltage source to the positive terminal. Moreover, there are two types of electricity.
Let’s delve into the topic of electricity and learn about it in detail.
Electricity
To know and understand electricity we have to go to the atomic level. An atom is the smallest particle of matter.
Atoms have positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons that revolve around the nucleus. These are called electric charges.
The atom’s electrons are not always attached to it. In some atoms, electrons are loosely bonded so they become free when an external force is applied.
This free movement of electrons is what we call electricity.
So,
Electricity is the flow of electric charges typically electrons.
For an electronic circuit to work properly and provide the intended output, movement of charges is needed and this movement of charges is electricity.
Types of electricity
There are two types of electricity, static electricity and current electricity.
Let’s discuss both types in detail.
1. Static electricity
When electric charges develop on the surface of the material that is what we call static electricity, this type of electricity can be made by rubbing the two materials together and creating friction.
Static electricity can make the objects attract each other or even cause a spark. For example, you are dragging your feet over a carpet.
When you rub or drag your feet on the carpet. You build up a positive charge as our body is a conductor and conductors lose their valance electrons easily. So due to the loss of electrons from the body, it becomes positively charged.
A carpet is an insulator, it never gives up electrons but can take electrons from conductors in this case from your body. This creates a charge imbalance between the carpet and your body so when you touch a metal object you get zapped.
The metal object is the conductor with loosely bound valance electrons, your body takes these electrons to restore charge imbalance.
2. Current electricity
Current is the flow of electrons so current electricity is produced due to the flow of electrons from one part of the circuit to another.
Static electricity can flow in any material but the current electricity flows through a conductor.
Starting a car, turning on the light, TV, and other appliances are some examples of current electricity. There are different sources to generate current electricity.
Below is a circuit, in which the battery provides the electric charges to light up the bulb.
The battery’s chemical reaction produces current electricity; another common source is a generator. In a basic generator, electricity is generated when a copper coil rotates within a magnetic field.
Current electricity is of two types, DC (Direct current) and AC (Alternative current).
AC and DC
DC electricity has a constant flow of electrons, which means the electrons flow in one direction. The electronic circuits utilized DC electricity.
On the other hand, AC is bi-directional electricity and changes the direction of charge flow means electrons flow in both directions. Our homes and places of business receive alternating current to power their electrical outlets.
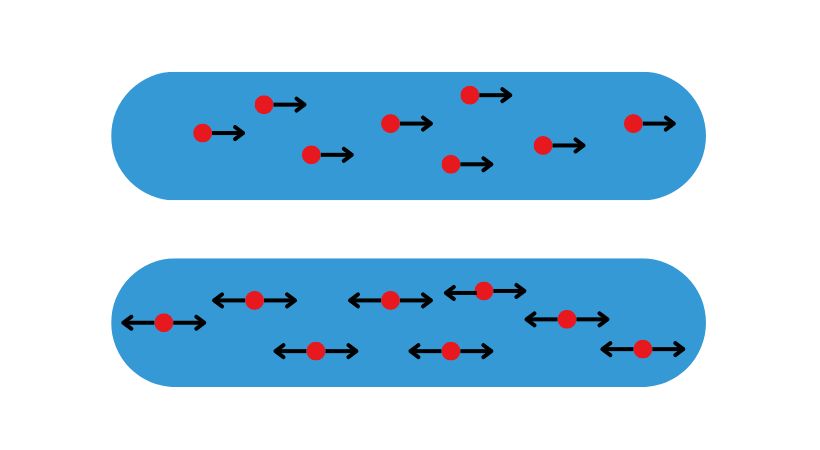
Since working with circuits is a must for working with electronics, and circuits are the means through which current electricity flows, we will concentrate on this sort of electricity throughout our learning process.
We will mainly focus on the DC type of current electricity in electronics.
Applications of Electricity
Electricity has various applications at home and in different industries. I’ll go into detail here about a few of the major uses of electricity:
1. Household appliances
In today’s world without electricity we can’t survive, to operate different home appliances like TVs, refrigerators, washing machines, electric stoves, ovens, air conditioners, and electric heaters we need electricity.

Lighting is among the most widespread and important uses of electricity. The use of gas lamps, candles, and other conventional light sources has mostly been superseded by electric lighting.
To generate light effectively, several types of bulbs, including incandescent, fluorescent, LED, and CFL, utilize power.
2. Communication
In our linked society, the utilization of electricity for communication is of the utmost importance.
Modern communication technologies, ranging from traditional landlines to the Internet and wireless networks, are all powered by electricity.
Charging different electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, and many other tools requires electricity to function.
Therefore, the role of electricity in communication cannot be overstated, as it serves as the foundation of our connected and information-driven society.
3. Electronics
Electricity is necessary for the operation of electronics, including computers, smartphones, and televisions.
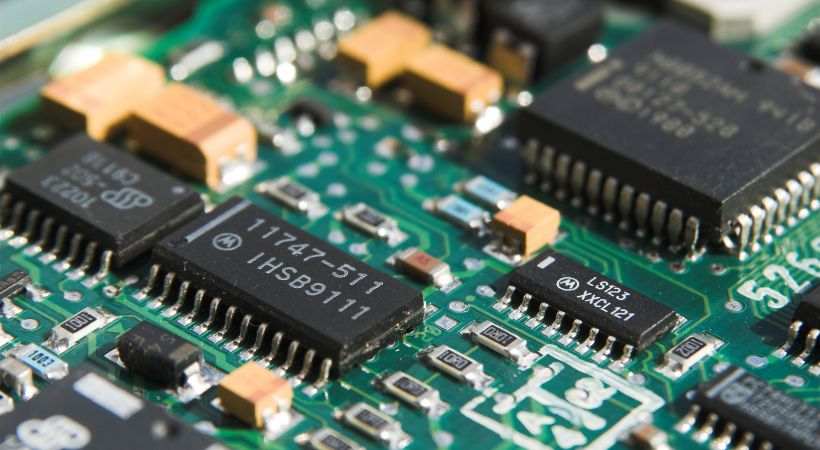

Electronic circuits require electricity to function as circuit is the logical combination of various electronic components. Electric currents are used by printed circuit boards (PCBs) and microchips to process and convey information.
Electrical signals are amplified and controlled by transistors, the fundamental components of contemporary electronics.
4. Healthcare
In hospitals, the tools and different devices operate by electricity. The surgical operation needs high-quality lights during operation and all these are possible due to electricity.
The X-ray, MIR machines, dialysis, and other devices are operable due to electricity. In every field of life, electricity plays an important role and has made our lives easier.
Conclusion
Electricity can be defined as a form of energy associated with the presence and flow of charged particles, typically electrons.
Atom is the smallest particle of matter and it consists of charged particles positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons. The flow of these particles is responsible for the generation of electricity.
Electricity has two types, static and current electricity. Static electricity is generated when you rub two materials and create a charge imbalance. The flow of electrons through the conductor or semiconductor produces current electricity.
Household appliances, healthcare instruments, electronic circuits, and today’s modern communication require electricity. These are some of the applications of electricity.
This was all about electricity.
Thank you…
Other useful posts:
