Hi. Hope you are having a good life. In this post, I share my knowledge about resistor basics and try to answer the question, why do we use resistors? Or in other words, what are the applications of resistors?
Hopefully, this post will help.
Why do we use resistors?
To my knowledge, a resistor is the part of almost every electronic circuit. You will probably see any circuit without it.
It is used for, current limiting, voltage division, feedback, pulling up or down floating voltages, gain control, and terminating loads.
In the rest of the post, I give more info about the mentioned applications.
Current Limiting
Let me tell you something very interesting about voltage and current. You can control voltage across your device, while current is something you cannot control, it is drawn by your device according to its need i.e. the value of its resistance.
If the resistance of your device does not change with anything i.e. temperature, and applied voltage.
Then you do not need any current limitation.
But if your device resistance does change with mentioned parameters then you need a current limiting resistor, to limit the current, to prevent your device from burning.
For example, in the case of an LED. The LED resistance changes with applied voltages.
We know an LED is a type of diode, it turns on when you apply the certain characteristic forward voltage (1.5 to 4 V for the case of LED).
The interesting thing is when you increase the forward voltage, the resistance of the LED decreases, and according to Ohm’s law the current start to increase. If we let the current to increase a certain limit, we may end in burring our beautiful LED.
Why?
Because as current increases the power also increases, and it is a fact, a device can handle a certain limit of power. If you exceed the limit you will burn it.
In summary, we use a current limiting resistor in series to any device or circuit, to ensure a specific amount of current is available for safe operation.
Voltage Division
You are an electronics hobbyist or expert person, you already know it is very unprofessional to have one circuit with more than one power supplies attached to it.
You probably did not see any of such circuit, nor want to design such a one your self. But how to solve this problem, one power supply and all the different voltage levels in the circuit.
For example, you have a 12V power supply, and in your circuit LED needs 5V, buzzer need 6V, amplifier need 9V, and the list goes on depending on your circuit.
The simple solution is the resistor voltage division circuits.
A resistor voltage divider is a simple circuit which divides the high input voltage into a small fraction i.e. from 12V to 5V or 12V to 6V etc.
You can power up all your circuit components with different voltage and current ratings from a single power supply using resistor voltage divider circuits.
Feedback Circuits
Feedback may be a little advance topic. It is a loop which connects output back to the circuit input to ensure safety, control and smooth operations.
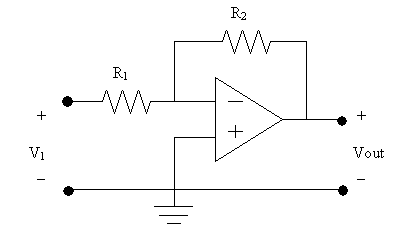
You may have heard of Opamps. The ideal one has very high open loop gain i.e. infinity, which in the practical leads the op amps to saturate.
You applied input 0f 10mVpp and open gain is infinity, the output theoretically should be infinity which is not possible. To handle this problem a negative feedback resistor (R2 in the above figure) is introduced to decrease the gain to practical limits.
A resistor is used in feedback circuits to reduce the high gain to certain safe limits.
Pulling up or Down Floating voltages
Resistors are used as pul up or down to ensure no floating pin left there in a microcontroller or any digital logic device.
The floating is a very common phenomenon in microcontrollers when a pin is left opened or unused.
For example, you have a microcontroller (MCU) with one pin configured as an input.
If there is nothing connected to the pin and your program reads the state of the pin, will it be high (pulled to VCC) or low (pulled to ground)? It is difficult to tell. This phenomenon is referred to as floating.
To prevent this unknown state, a pull-up or pull-down resistor will ensure that the pin is in either a high or low state, while also using a low amount of current. (Sparkfun)
Terminating Load
Terminating load is very useful when testing a certain circuit. For example, you designed a power supply for a specific load. Let say the load is 10k. You can verify your design by just simply terminating the power supply output with 10kOhm resistor.
You can also test for other loads too to determine the worst possible cases.
In microwave circuits, if you do not terminate the output with match load resistor i.e 50Ohm. You will have all your waves reflect back making standing waves in the transmissions lines.
Besides microwaves circuits, in communication termination is used to ensure recessive bit transmission. It also prevents reflections that might cause communication failure as a result of ringing on the bit edges.
Gain Controller
Resistor plays a key roll in gain control of many circuits. In the design of common collector (CE), the gain is directly proportional to the value of collector resistor value. The larger the resistor value the larger the gain, but you cannot increase its value to certain limits.
This all I want to answer the question, why do we use resistors in circuits.
I will keep updating it as I learn new things about the resistors. Feel free to comment if you have any question. You can also add more value to it by sharing your knowledge in the comment section. Share it with other people to help them as well, and see you in the next post.
Thank you and have a happy life.
**To know some answer about resistor here is a quick post for you explore, resistor questions and answers